Clustering Coefficient Of Random Graph
So the clustering the general formula for clustering coefficient of a random graph is the average degree of a node. Begingroup Conventionally you say that any graph with no connected triplets has a global clustering coefficient of 1.

Clustering Coefficients C Of Spin Glass Graphs Of Bipartite Random Download Scientific Diagram
The clustering coefficient is a real number between zero and one that is zero when there is no clustering and one for maximal clustering which happens when the network consists of disjoint cliques.

Clustering coefficient of random graph. This means the three triplets in a. Here we study a wider class of random intersection graphs than the one considered by them and give the asymptotic value of their clustering coefficient. Suppose that a vertex v has k v neighbours.
A triplet consists of three connected nodes. My claim about clustering coefficient distribution with respect to. The clustering coefficient C p is defined as follows.
As you say there are various conflicting definitions of clustering coefficient. Global clustering coefficient. To compute C n we use the number of triangles a node is a part of T n and the degree of the node d nThe formula to compute the local clustering coefficient is as.
While it is easy to see that the expected mean local clustering coefficient is p see next section the expected global clustering coefficient is not identically p for any n. For node with degree we compute the clustering coefficient as. Check the paper and see if it corresponds to yours.
Mboxif k text is even 0 mboxif k text is odd endcases c Show that the clustering coefficient is C frac12c1 where C is definite as three number of triangles over the number of connected triples. Where is the number of edges between the neighbors of node. The global clustering coefficient is based on triplets of nodes.
The average clustering coefficient of a graph G is the mean of local clusterings. The local clustering coefficient C n of a node n describes the likelihood that the neighbours of n are also connected. Im doing some research and Ive come to a point where I have calculate the clustering coefficient of a graph.
Edge-dual graphs of Erdos-Renyi graphs are graphs with nearly the same degree distribution but with degree correlations and a significantly higher clustering coefficient. Compute the ACC average clustering coefficient of G_fb consult the NetworkX manual or the video lecture for the correct function which does it av_clust_coeff. Evidence suggests that in most real-wor Clustering Coefficient in Graph Theory.
Choose a node at random choose two of its neighbors at random and check if. I do understand that the degree distribution in the case of a random network shows a Poisson behavior but dont understand why the clustering coefficient shows no change with degree. For example for n3 C_GC 1 only when all edges are present with probability p3 and is otherwise zero with probability 1-p3.
In the context of random intersection graphs the clustering coefficient was first studied by Deijfen and Kets Eng Inform Sci 23661674 2009. For random graphs the clustering coefficient is equal to graph generating connection probability Cp since the probability of first neighbours being connected is constant for all nodes. Simulating random graphs with tunable clustering is non-trivial.
Generate edges in G_rand at random. By the way you will find. This function finds an approximate average clustering coefficient for G by repeating n times defined in trials the following experiment.
A triangle therefore includes three closed triplets one centered on each of the nodes nb. Also the clustering coefficient is undefined for nodes with degree 0 or 1. For j in range0i.
Its value depends on what the random graph ends up being. I came up with a graph generation model that can easily generate connected random graphs of some 10000 nodes and more that follow prescribed degree and local clustering coefficient distributions which can be chosen such that any desired global clustering coefficient results. In any case you will need to.
P_k begincases e-cck2k2. First we initialize it. Even if you restrict the space of graphs to those with at least one connected triplet you have for n3 an expected global clustering coefficient of p3 p3 31-pp2 which is not p2.
Theres a chance that the parameter is very big and theres a chance that its very small based on what the random graph ends up being. But that aside the whatever parameter of a random graph is a random variable with a distribution. In percolation theory one examines a finite or infinite graph and removes edges or links randomly.
In real networks the clustering coefficient is much larger than in case of random graphs of equal size equal number of nodes and edges. The number of edges connecting a vertexs neighbors the total number of possible edges between the vertexs neighbors. Now we have to generate a random graph.
The clustering coefficient measures how connected a vertexs neighbors are to one another. For i in range0k. Begingroup What is the clustering coefficient.
The clustering coefficient for undirected graphs measures what proportion of node s neighbors are connected. The Local Clustering Coefficient algorithm computes the local clustering coefficient for each node in the graph. In graph theory a clustering coefficient is a measure of the degree to which nodes in a graph tend to cluster together.
You can find a short description here. And we take the average degree at which the degree of a node is just the number of connections it has remember that. Then at most k v k v -1 2 edges can exist between them this occurs when.
More specifically it is calculated as. One method is that described by Newman. Request PDF The Clustering Coefficient of a Scale-Free Random Graph We consider a random graph process in which at each time step a new vertex is added with mm out-neighbours chosen with.
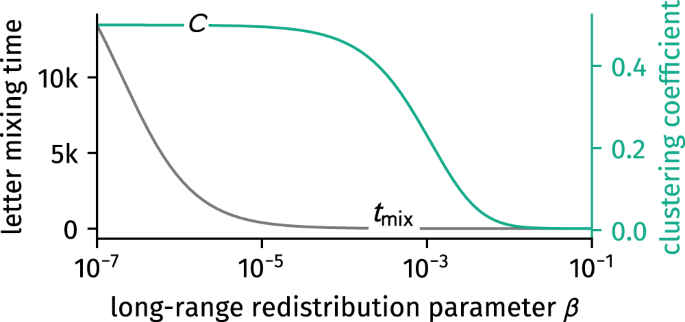
Generalization Of The Small World Effect On A Model Approaching The Erdos Renyi Random Graph Scientific Reports
Snap Higher Order Clustering Coefficient
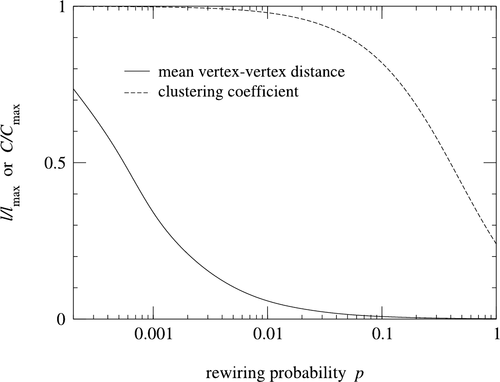
Measuring Networks And Random Graphs
Posting Komentar untuk "Clustering Coefficient Of Random Graph"